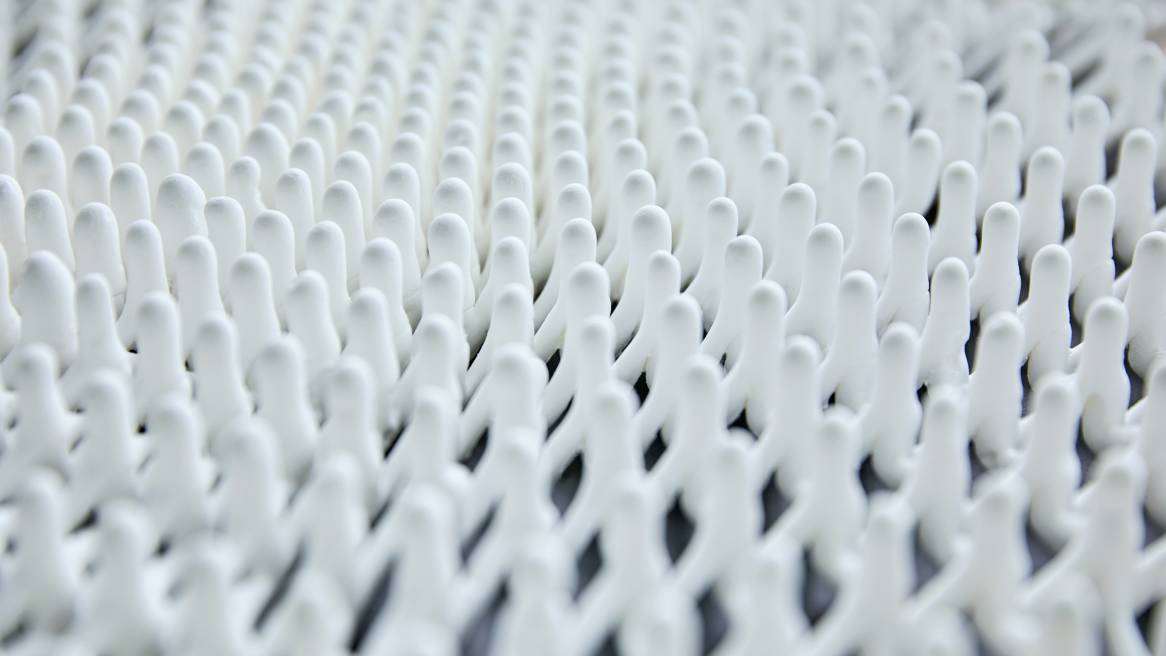
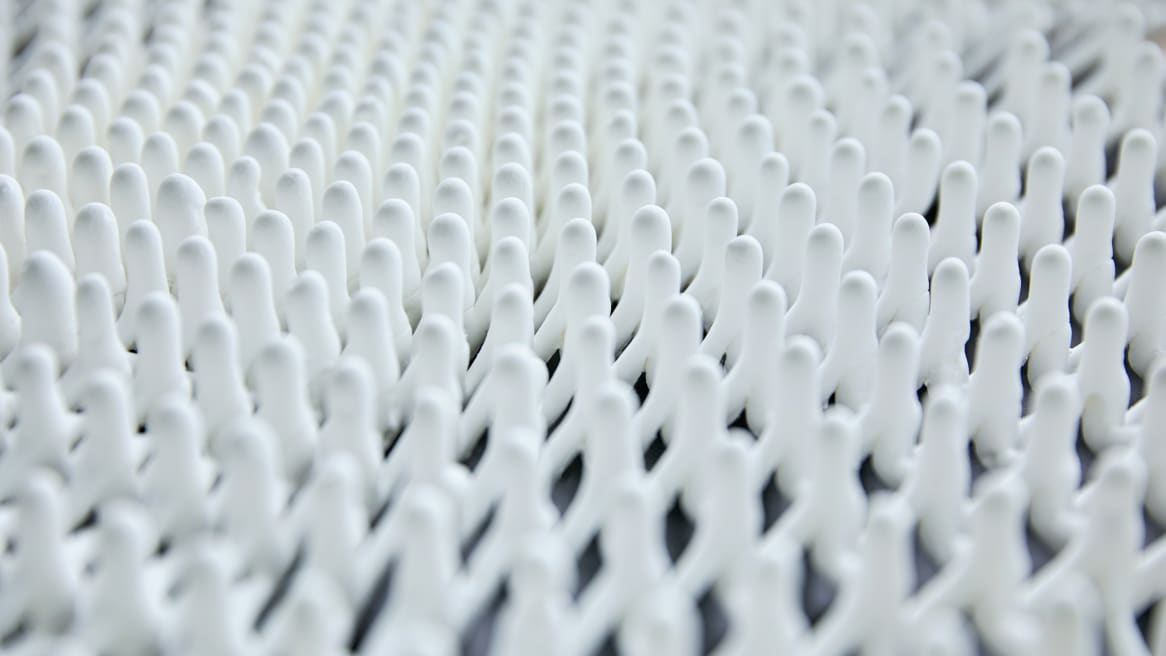
MIT Lab + Steelcase Yield 3D Printing Breakthrough
MIT’s Self-Assembly Lab, Steelcase and award-winning product designer Christophe Guberan collaborated to create a new 3D printing process unveiled at Milano Design Week. The technology breaks the three constraints of traditional 3D printing by using a rapid liquid printing technique enhancing speed, scale and quality. The partnership between MIT, Steelcase and Guberan explores the future of furniture personalization and the opportunities for customization through innovation.
Why Customization?
People around the world are rejecting the stereotypical, monolithic office their employers are creating. In order to attract and retain high-skilled talent, as well as improve employee wellbeing and engagement , many organizations are realizing they need to rethink their workplace to deliver a more human-centered experience. Work environments that allow for furniture customization can increase a person’s sense of belonging, promote self-expression and authenticity.
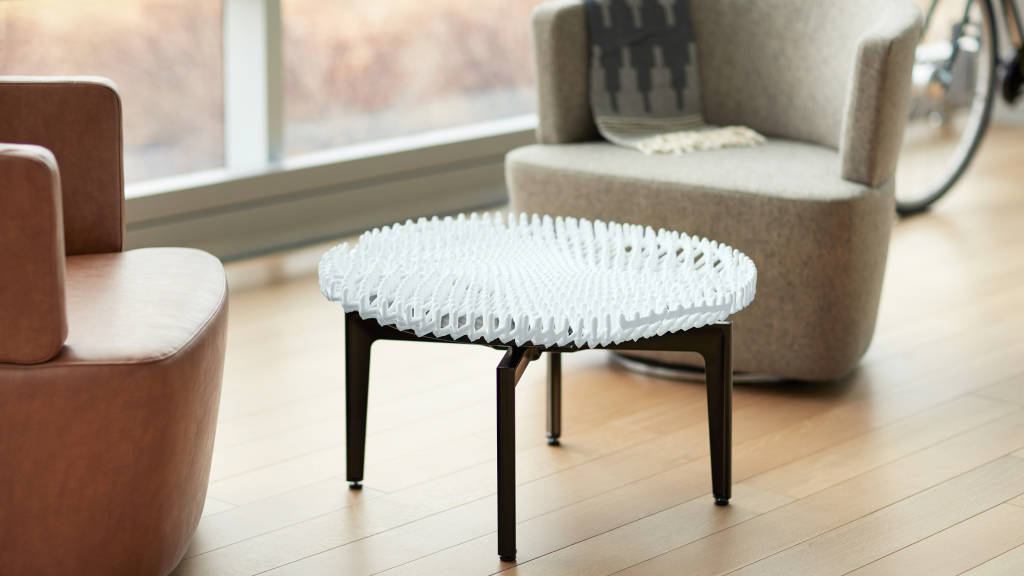

Turnstone, a Steelcase brand, is focused on delivering these kinds of personalized experiences to today’s workers. In 2016, it’s Bassline table collection, designed to support nearly any surface the customer desires, won a Best of NeoCon Innovation Award. It’s unique design enabling unprecedented personalization made it a natural fit for the 3D printing experiment with MIT’s Self-Assembly Lab.
What’s New?
Three dimensional printing has been around for decades. But, it always comes with certain limitations. It requires a support structure, layering and curing to create objects. Those needs lend themselves to a slow, small-scale and low-quality process. The Self-Assembly Lab, founded by MIT assistant professor Skylar Tibbits, and co-directed by Jared Laucks, aimed to create a new process improving on speed, size and quality material.
“Industry partners are really important for us,” says Tibbits. “They bring insight, challenges, relevance and domain expertise that we don’t have.”
An innovative new technique emerged after months of working on the project with Steelcase. The process prints inside of a gel — essentially allowing a product designer to draw in 3D space without the limitations of gravity. Because there is no traditional support material and structure or layering, the printing process is much faster and can be as big as the machine available. There’s also a two-part mixing process allowing the material to be chemically-cured instead of set using light or temperature. The technique mixes, extrudes and cures all while the 3D printing is underway.
Rapid Liquid Printing
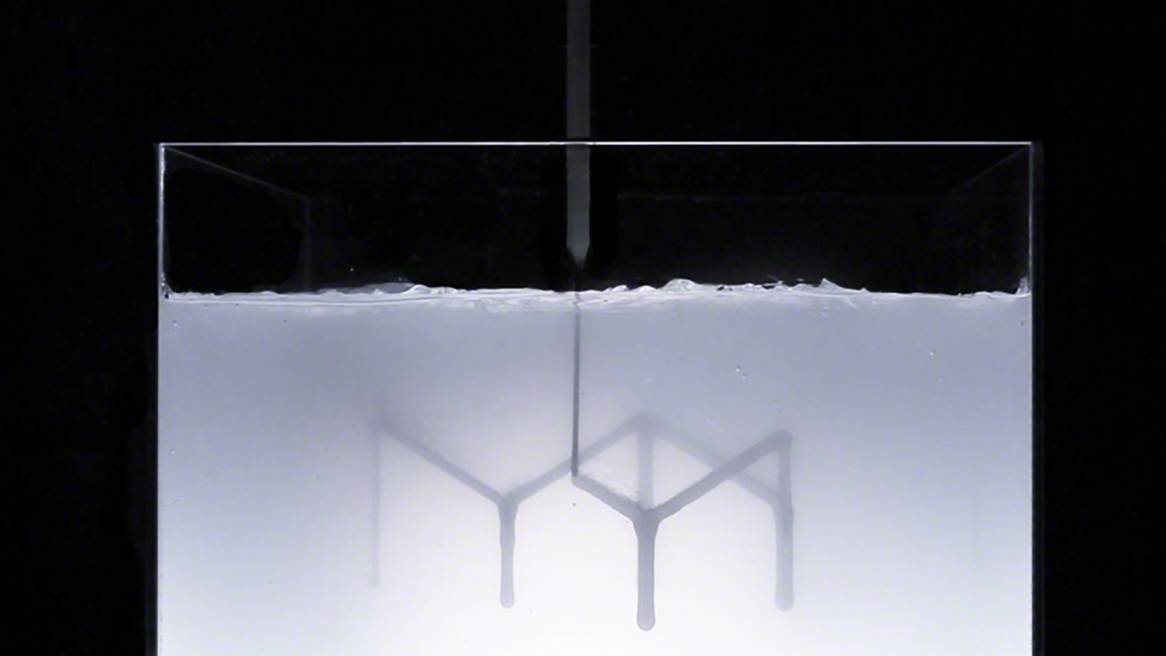

At Milano Design Week, MIT’s Self-Assembly Lab team and Christophe Guberan exhibited the process behind the table top created using this breakthrough 3D printing process. Tibbits said it took about 28 minutes to print the intricate design for the Bassline table top. In another experiment, the team was able to print a structure in 10 minutes with Rapid Liquid Printing that had previously taken 50 hours to produce using a different 3D process. The type of design, material and size all impact printing speed.
What’s Next?
This new printing process, though an experiment now, shows the potential for using a class of materials in the future that have the same properties as real world products.
“As a designer, what’s most fascinating and unique about Rapid Liquid Printing is the line quality of the print. It’s soft, almost organic. It evokes images of brushstrokes or the branches of plants,” says Yuka Hiyoshi, turnstone senior industrial designer. “The printing speed is very impressive. In the far future, large scale objects could be printed in minutes instead of days. Also, it’s not limited to typical 3D printing material making the technology very desirable from a design perspective.”
The collaboration between Steelcase and MIT will continue to seek further answers regarding materials, scale and improved printing processes. It will also be important to figure out the optimal product or object to print – one that takes the best advantage of this new process.
Steelcase and MIT are long-term research partners with a rich history of exploring the future of the workplace. Though the work continues to be in exploration, this collaboration responds to the need for the workplace to provide a greater sense of informality, authenticity and one-of-a-kind products and experiences.